The compressive strength of PEEK (Polyetheretherketone) has gained significant attention in various engineering applications, particularly in the aerospace and medical fields, due to its remarkable thermal stability and mechanical properties. According to a report by the International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, PEEK exhibits compressive strength values often exceeding 100 MPa, making it an ideal candidate for high-performance environments where resistance to deformation under load is crucial. The demand for materials that can withstand extreme conditions while providing reliability has pushed researchers and engineers to delve deeper into the specific methods of measuring these properties accurately.
Understanding how to measure the compressive strength of PEEK is paramount for optimizing its application in critical sectors. A comprehensive study published in the Journal of Materials Science emphasizes that the variability in the processing conditions and morphological structure significantly influences the compressive strength of PEEK. Thus, establishing standardized testing procedures is essential not only for ensuring and enhancing product quality but also for facilitating comparisons across different materials and conditions. By focusing on accurate measurement techniques and their implications, this article aims to contribute to the growing body of knowledge necessary for maximizing the performance potential of PEEK in various applications.

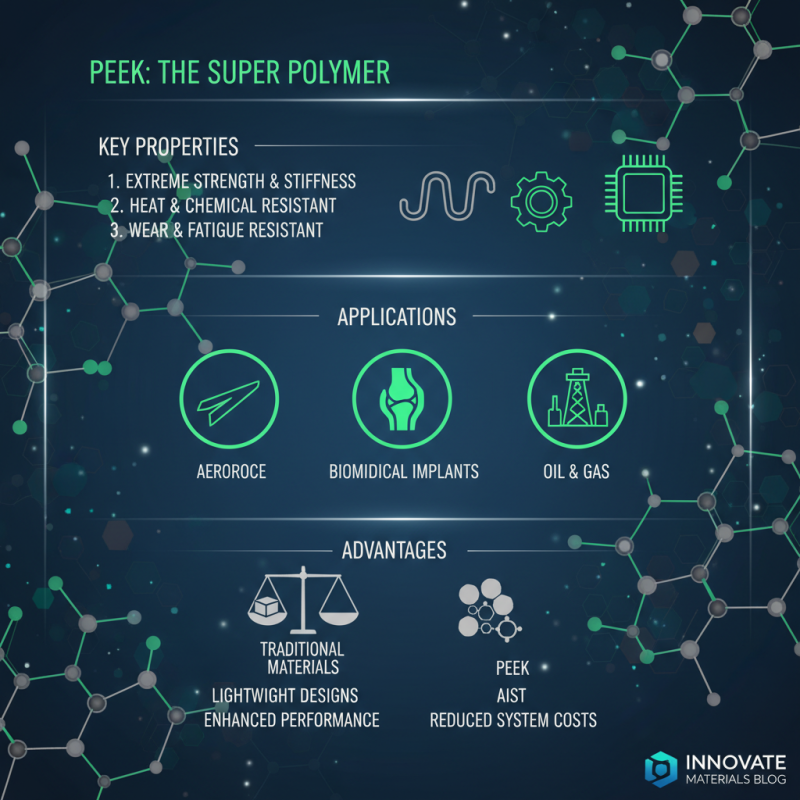
PEEK, or polyether ether ketone, is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its exceptional mechanical properties and resistance to heat, chemicals, and wear. This unique polymer stands out in the engineering field due to its ability to maintain dimensional stability and strength in demanding environments, making it an ideal choice for applications ranging from aerospace to biomedical devices. The importance of understanding PEEK material lies in its capability to replace traditional metals and ceramics, ultimately leading to lightweight and more efficient designs that enhance performance and reduce overall system costs.
In engineering, the compressive strength of materials significantly influences their selection for structural applications. PEEK exhibits high compressive strength and stiffness, which allows it to withstand significant loads without permanent deformation. Measuring its compressive strength accurately is crucial for engineers to ensure that components made from PEEK can perform reliably under operational stresses. Different testing methods, such as ASTM D695, provide standardized procedures for evaluating the compressive properties of PEEK, enabling engineers to make informed decisions when utilizing this material in critical applications where performance and reliability are paramount.
Preparing for compressive strength testing of PEEK samples is crucial to obtaining accurate and reliable results. The first step involves ensuring that the PEEK specimens are of uniform dimensions and free from any surface defects. Samples should be machined or cut according to standardized shapes, such as cylinders or rectangular prisms, to minimize variability in testing. It is essential to control for any environmental factors, such as temperature and humidity, that could affect the material properties during the testing phase.
Next, the samples must undergo proper conditioning before testing. This may involve drying the PEEK samples to remove moisture that could impact the compressive strength. Conditioning may also include exposing the materials to specific temperatures that reflect the intended application environment. After conditioning, the samples should be weighed and measured for precise dimensional data, which is critical for calculating the compressive strength accurately. Proper preparation is key to ensuring that the testing procedure mirrors real-world applications and yields meaningful insights into the performance of PEEK in various engineering contexts.
| Sample ID | Preparation Method | Sample Size (mm) | Compressive Strength (MPa) | Test Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 001 | Injection Molding | 20 x 10 x 10 | 100.5 | 2023-10-01 |
| 002 | Compression Molding | 25 x 15 x 5 | 95.2 | 2023-10-02 |
| 003 | 3D Printing | 30 x 10 x 10 | 98.7 | 2023-10-03 |
| 004 | Extrusion | 40 x 20 x 3 | 85.6 | 2023-10-04 |
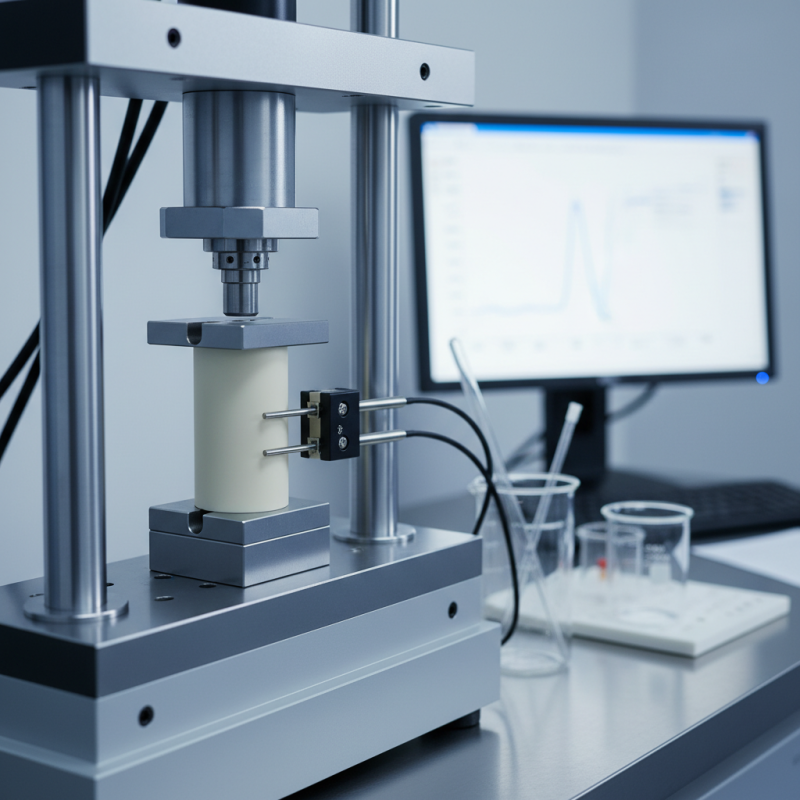
When measuring the compressive strength of polyether ether ketone (PEEK), several key testing methods are employed to ensure the material meets optimal performance standards. One common approach is the use of a universal testing machine (UTM), which applies a uniaxial load to a standardized specimen of PEEK. This method allows for precise control over the load application and provides clear data regarding the material's elastic modulus, yield strength, and ultimate compressive strength.
Another effective technique involves utilizing a hydrostatic pressure test, which evaluates the compressive strength by subjecting the PEEK sample to extreme pressure in a controlled environment. This method is particularly useful in simulating conditions that the material may encounter in real-world applications, such as in aerospace or automotive components. Additionally, dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) can be utilized to assess the viscoelastic properties of PEEK under compressive loads, providing insights into how the material performs under varying temperature and frequency conditions. Collectively, these methods offer a comprehensive analysis of PEEK’s compressive strength, paving the way for its optimal application in demanding environments.
The compressive strength of polyether ether ketone (PEEK) is a critical factor in its application, especially within industries that demand high-performance materials such as aerospace, medical, and automotive sectors. To effectively analyze and interpret the results from compressive strength tests, it is essential to understand the underlying methodologies and the implications of the measured data. According to recent industry reports, PEEK exhibits impressive compressive strengths typically ranging between 80 to 100 MPa, which is significantly superior to many thermoplastics—making it a preferred choice for structural applications.
Interpreting compressive strength test results requires a comprehensive approach, taking into account variables such as sample preparation, testing conditions, and environmental influences. The ASTM D695 standard is widely adopted for these tests, establishing a framework that ensures the reliability and reproducibility of results. It is also vital to consider factors such as the rate of load application and temperature, as they can significantly affect the material's performance under stress. For instance, studies indicate that PEEK’s compressive strength can decrease at elevated temperatures, highlighting the importance of conducting tests within the specified operational conditions to avoid misleading conclusions. By adhering to these standards and methodologies, engineers can optimize the utilization of PEEK in demanding applications, ensuring both safety and performance.

When evaluating the optimal performance of Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK) in engineering applications, understanding its compressive strength is paramount. Compressive strength not only dictates the material’s durability under load but also informs design decisions for components used in sectors like aerospace, automotive, and medical devices. A recent report from the Polymer Research Institute indicates that PEEK exhibits a compressive strength ranging from 90 to 100 MPa, making it exceptionally suitable for high-performance applications. Optimizing the use of PEEK based on such strength findings can lead to enhanced reliability and longevity of end products.
For users seeking to manipulate PEEK's properties, it is essential to integrate testing processes that analyze how variations in temperature and chemical environment affect its compressive strength. A study published in the Journal of Materials Science highlighted that the compressive strength of PEEK can significantly improve when post-processing treatments, such as annealing, are applied. Understanding these nuances allows engineers to tailor their applications, ensuring they achieve maximum performance while maintaining material integrity.
Tips: Always conduct thorough materials testing before finalizing the design to ensure that the selected PEEK meets the required compressive strength for specific applications. Regularly review relevant research reports to stay updated on the latest findings and innovations that can enhance PEEK's performance in critical applications. Additionally, consider collaborating with materials scientists to explore novel formulations that could improve PEEK's mechanical properties further.