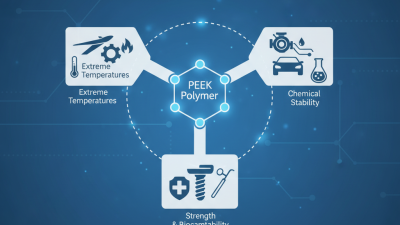
In recent years, the significance of PEEK material composition has grown across various industries. Dr. Jane Smith, a renowned expert in advanced materials, states, "Understanding PEEK material composition is key to harnessing its full potential." This statement highlights the foundational role that material composition plays in applications ranging from aerospace to medical devices.
PEEK, or polyether ether ketone, is celebrated for its exceptional mechanical properties and chemical resistance. Its high thermal stability makes it suitable for demanding environments. Industries are increasingly recognizing the value of PEEK, yet many remain unaware of its diverse applications and the factors influencing its performance.
For example, in the aerospace industry, weight reduction can lead to significant gains in efficiency. Engineers must carefully consider PEEK material composition to achieve these benefits. However, the complexity of these materials often leads to misconceptions. There is a need for continuous education and understanding in this evolving field. The journey of mastering PEEK material composition is just beginning.

Polyether ether ketone, commonly known as PEEK, is a high-performance thermoplastic. Its unique structure provides excellent mechanical strength and thermal stability. PEEK can withstand extreme temperatures and harsh environments. This makes it ideal for demanding applications across multiple industries.
In aerospace, PEEK is often used for components such as bearings and insulators. The material's light weight reduces fuel consumption. In the medical field, PEEK is valued for its biocompatibility. Surgical instruments and implants made from PEEK are dura ble and reliable. Its resistance to chemicals is another notable benefit. However, manufacturing with PEEK can be costly. This raises questions about its accessibility in various applications.
PEEK's exceptional properties make it attractive, yet challenges persist. For instance, its high melting point requires specialized processing equipment. This limits its use in industries with tighter budgets. Additionally, workers must be trained to handle the material properly. Despite these challenges, many industries are finding innovative ways to utilize PEEK. There remains ongoing exploration into optimizing its applications for better efficiency.

Polyether ether ketone, or PEEK, stands out in various industrial sectors for its remarkable properties. In aerospace, it enables lightweight and durable components, essential for fuel efficiency. PEEK parts often withstand extreme temperatures and pressures, essential in flying conditions. Yet, the costs can be a hurdle for some projects. It's crucial to analyze whether the performance justifies the investment.
In the automotive sector, PEEK is increasingly used for engine components and valves. Its resistance to wear and chemicals ensures longevity. The material helps reduce vehicle weight, improving overall performance. However, manufacturers must balance cost and benefit; PEEK’s high price may not suit every application.
In medical applications, PEEK shines as a biocompatible material. Implants and surgical instruments benefit from its strength and sterilization capabilities. Yet, there are ongoing debates about its long-term effects in the body. Some suggest more extensive studies are needed. Choosing PEEK for medical use must involve careful consideration of these factors.
PEEK (polyether ether ketone) is gaining traction in electrical insulation and electronics manufacturing. Its high thermal stability makes it a choice material for various applications. This thermoplastic can withstand extreme temperatures while maintaining robust mechanical properties. In electronics, this is crucial. Components must work reliably under heat stress.
The dielectric properties of PEEK also contribute to its appeal in insulation. It offers low electrical conductivity, which is vital for separating conductive pathways. Insulated wires and connectors require materials that can withstand both heat and electric fields without failing. PEEK achieves this balance effectively. However, its processing can be challenging. It requires specific techniques that not all manufacturers use. There can be a learning curve.
Another point of consideration is cost. PEEK is a premium material. Budget constraints can limit its use in some sectors. While many industries benefit from its properties, others may hesitate. The trade-off between cost and performance is a recurring theme. Manufacturers must weigh the benefits against their financial limits. This complexity adds depth to its applications.
This chart illustrates the composition of PEEK (Polyether ether ketone) and its key applications in various industries, particularly focusing on its role in electrical insulation and electronics manufacturing.
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) is a high-performance polymer known for its strength and thermal stability. It excels in demanding applications across various industries. PEEK stands out when compared to other polymers such as polyamide and polyimide. Many industries favor it due to its exceptional resistance to chemicals and heat.
Polyamides are widely used, but they lack the high temperature resistance PEEK offers. PEEK can withstand temperatures up to 250 degrees Celsius, while polyimides can only endure around 200 degrees Celsius. This difference is crucial for applications in aerospace or automotive sectors.
While PEEK has its advantages, it is also more expensive than some alternatives. Cost can be a barrier for smaller companies. Moreover, PEEK can be challenging to process, calling for specialized equipment. This complexity can deter potential users. Even with its remarkable qualities, some industries still rely on traditional materials. Choices can be influenced by budget and processing capabilities.
The future of PEEK material development looks promising. As industries diversify, the demand for advanced materials grows. PEEK, known for its strength, chemical resistance, and thermal stability, excels in various applications. Emerging sectors, such as electric vehicles and aerospace, will play a significant role in driving innovation.
Tips: Consider evaluating the compatibility of PEEK with other materials in your projects. This can enhance its performance in specialized applications.
In addition, sustainable practices are becoming vital. Recycling PEEK materials could reduce waste and environmental impact. Research is ongoing to improve processes that can reclaim and reuse this high-performance plastic. There is room for exploration here.
Tips: Stay updated on advancements in sustainable practices. Engaging in community discussions can spark new ideas.
Moreover, the healthcare sector is exploring PEEK’s biocompatibility. Applications in medical devices show potential. However, challenges in sterilization and durability must be addressed. Dialogue within the scientific community helps identify these hurdles and brainstorm solutions.
| Property | Value | Industry Application |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Stability | Up to 260°C | Aerospace, Automotive |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Chemical Processing, Oil & Gas |
| Mechanical Strength | High | Medical Devices, Electronics |
| Friction Coefficient | Low | Manufacturing, Aerospace |
| Density | 1.3 g/cm³ | Automotive, Electrical Engineering |